Benefits of Wool
 Although wool has been used for tens of thousands of years, wool is a unique material that hasn't been replicated by modern technology. It's properties vary greatly and in many different, useful areas.
Although wool has been used for tens of thousands of years, wool is a unique material that hasn't been replicated by modern technology. It's properties vary greatly and in many different, useful areas.
WHY IS REPLACING PEAT MOSS SO IMPORTANT?
Peat moss has a long history in gardening. It's used extensively in soil mixes, outdoor and indoor gardening. Its main function is to retain water for plants. What's seen as a benefit to plants is actually a big problem for the environment. Even sustainably harvested peat-moss is not a long term solution. Peat moss grows 1mm a year, far less than is needed for the industry. According to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (ICUN):
- Peatlands are a type of wetland which are critical for preventing and mitigating the effects of climate change, preserving biodiversity, minimising flood risk, and ensuring safe drinking water.
- Peatlands are the largest natural terrestrial carbon store. They store more carbon than all other vegetation types in the world combined.
- Damaged peatlands are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, responsible for almost 5% of global anthropogenic CO2 emissions. Peatland restoration can reduce emissions significantly.
- Countries should include peatland conservation and restoration in their commitments to international agreements, including the Paris Agreement on climate change.
- Worldwide, the remaining area of near natural peatland (over 3 million km2) sequesters 0.37 gigatonnes of CO2 a year . Peat soils contain more than 600 gigatonnes of carbon which represents up to 44% of all soil carbon , and exceeds the carbon stored in all other vegetation types including the world’s forests.
source: https://www.iucn.org/resources/issues-brief/peatlands-and-climate-change
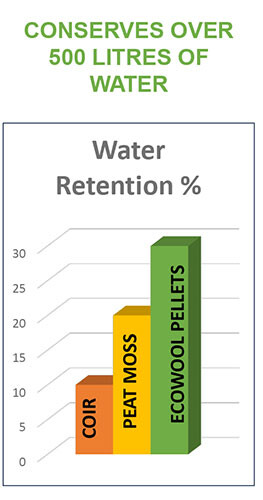
HOW IS WOOL BETTER THAN PEAT?
Wool is harvested annually and most sheep will grow well over 3 cm of wool annually. If you have ever lifted a wet wool sweater out of the laundry, you'll have an idea of how much water wool absorbs.
HOW DOES WOOL COMPARE TO MANURE?
Wool is an amazing fibre. It has a lab tested NPK of 10.54-0.06-3.64 . It's high nitrogen content means it has a lot of potency but because of the time it takes to break down it is less damaging to plants. Pellets begin breaking down in the soil in 2-3 months depending on the conditions. The long breakdown time provides a sustained nitrogen source for plants to thrive that can be seen from one season to the next. Manure breaks down much faster and provides a quick nitrogen boost but doesn't sustain it.

LAB ANALYSIS OF WOOL PELLETS:
Done by SGS Labs of Guelph.

Some interesting international studies and reports about wool, it's properties, uses, benefits, and potential that the above information was sourced from.
C. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4395/12/5/1210
D. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0956053X09000828?via%3Dihub
